What is laparoscopic surgery?
Laparoscopy is a surgical aproach used in the surgical treatment of the abdominal organs without large surgical incisions. Long-thin surgical instruments are used through several (3-5) small (<1 cm) holes during laparoscopic surgery.
In laparoscopic surgery, a camera enters the abdomen from one of the trocars, and a 3D view is obtained with a magnification of 10-15 times and in HD quality, even in some devices. This situation provides a very serious advantage over open surgery.
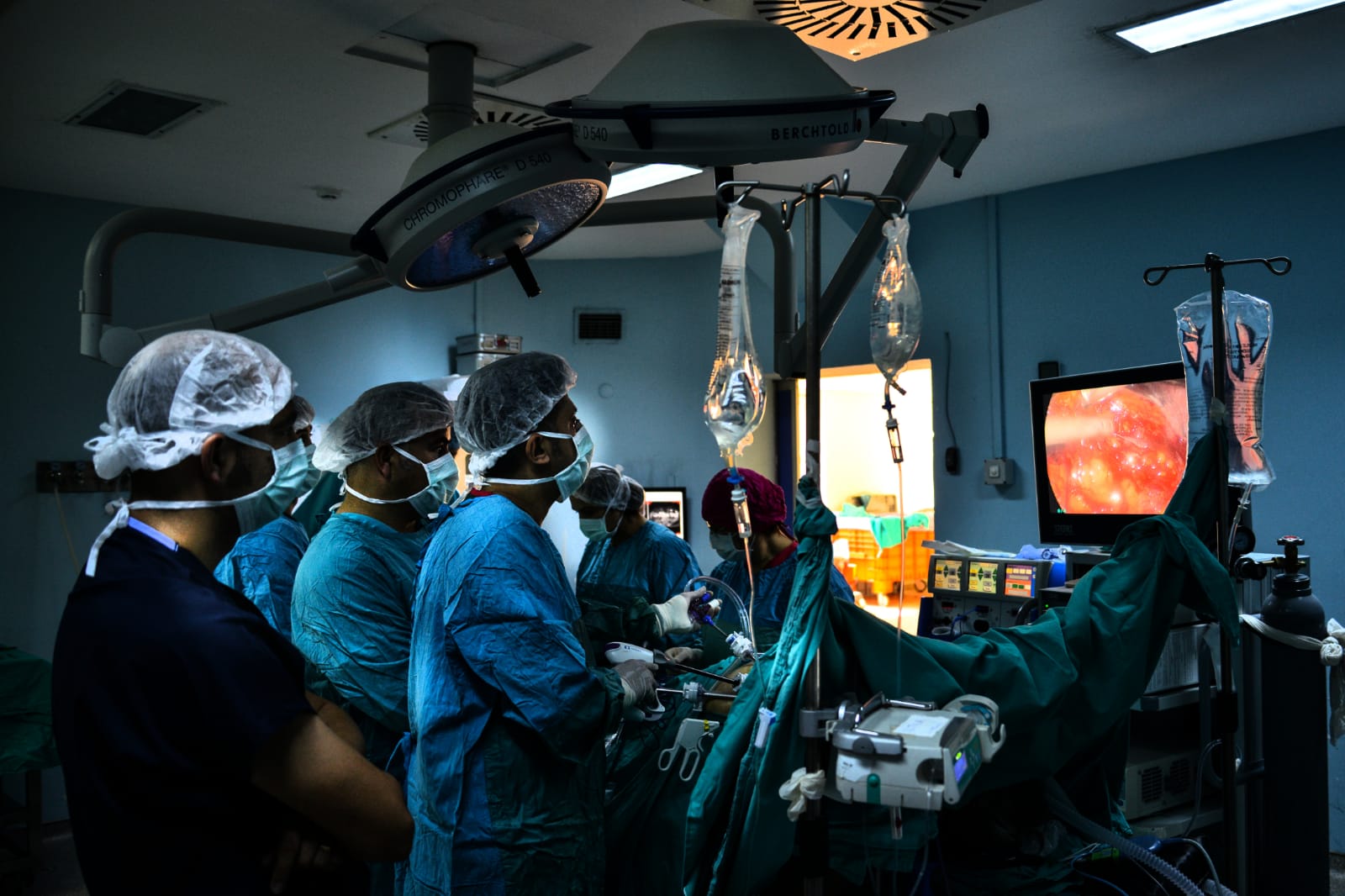
Having very small wounds after laparoscopic surgeries is both a cosmetically important plus, and it causes little discomfort and pain compared to large surgical incisions in open surgery. With the laparoscopic approach, postoperative pain and the use of painkillers, hospital stay and recovery time are considerably shortened.
Laparoscopic surgeries are performed under general anesthesia (narcosis).
Although laparoscopic surgery provides very important advantages compared to open surgery, the experience of the surgeon is important for its implementation. Because, we can say in the light of academic data that the complications decrease as the experience increases. Approximate complication rate in laparoscopic surgery is 5%. The mortality rate seen during laparoscopic surgery is about 0.3%; The probability of switching to open surgery is approximately 1-5%.
What are the benefits of laparoscopic surgery?
- Less bleeding during and after surgery
- Less postoperative pain
- Shortening the length of stay in the hospital
- Cosmetic appearance is more acceptable (small scar)
- Early return to daily activities and business life
What are the application areas of laparoscopic surgery?
Kidney cancer (Laparoscopic Radical nephrectomy), testicular cancer (Laparoscopic Retroperitoneal Lymphadenectomy), prostate cancer (Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy), bladder cancer (Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy), kidney outlet obstruction-UPJ stenosis- (Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty), removal of non-functioning kidneys (Laparoscopic Nephrectomy), adrenal gland (adrenal) tumors (Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy), ureter strictures (Laparoscopic uretero-neocystostomy, Laparoscopic Boari flap application, Laparoscopic Psoas Histch technique, Laparoscopic uretero-ureterostomy), stone surgeries (Laparoscopic pyelolithotomy, laparoscopic uretelolithotomy) are main usage areas for laparoscopic surgery.


